3. Hub
The NIC sends signals out in "packets". You can find out more about how a packet is put together on our section on packet switching.
If a network only has two devices to connect together then it is pretty easy to tell where packets are going as there is only one possible destination in either direction.
But once you connect more computers to the network, you need a device to sort out where all of these packets need to go, and also, how they will get there.
There are a number of different hardware solutions to this problem. The simplest, and least expensive, is a hub.
A hub is a hardware device that connects multiple devices in a network. All traffic has to pass through the hub. On large networks, you can have two or more hubs connected together.
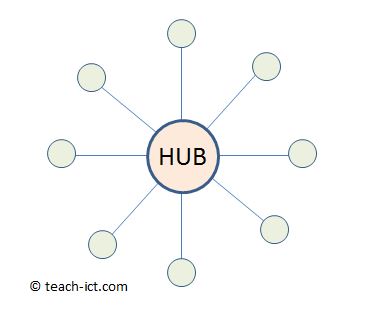
When the hub receives a packet of data, it re-broadcasts the packet to every other connected device. This ensures that the data gets to where it needs to go.
This method works well on small networks, but as more nodes are added, it becomes inefficient. This is because network cables can only carry one signal at a time. As the hub continues to send out redundant data packets, data collisions begin to occur. The data collisions in turn, affect the network's performance.
To overcome this issue, a switch is often used to replace the hub.

Challenge see if you can find out one extra fact on this topic that we haven't already told you
Click on this link: What is a network hub
